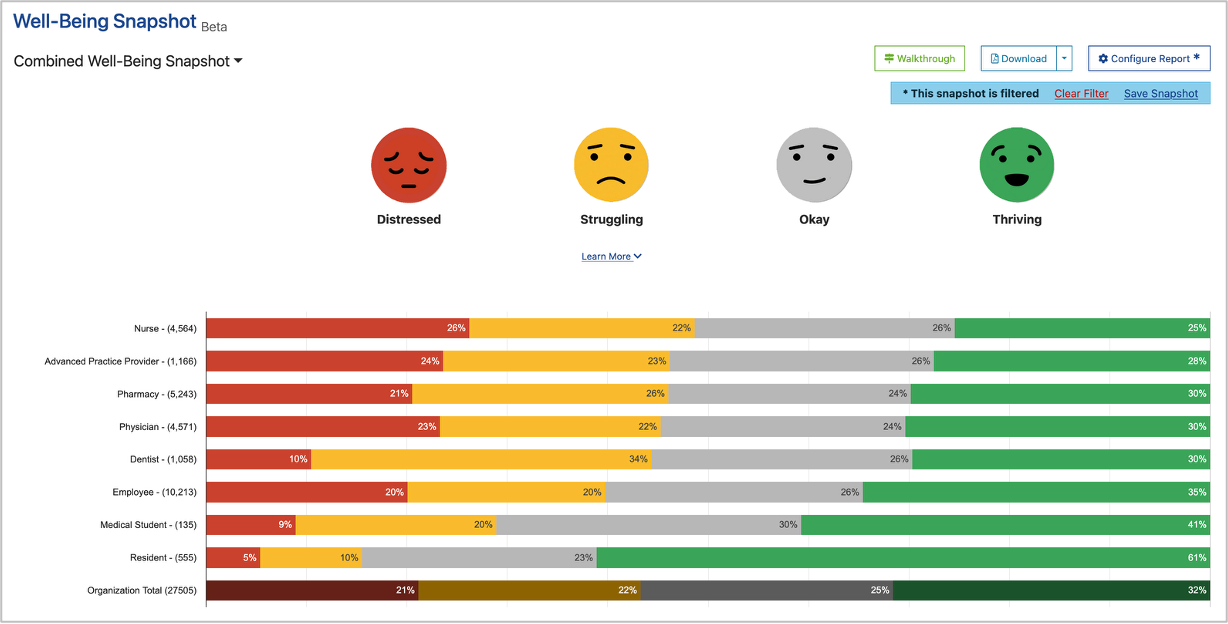
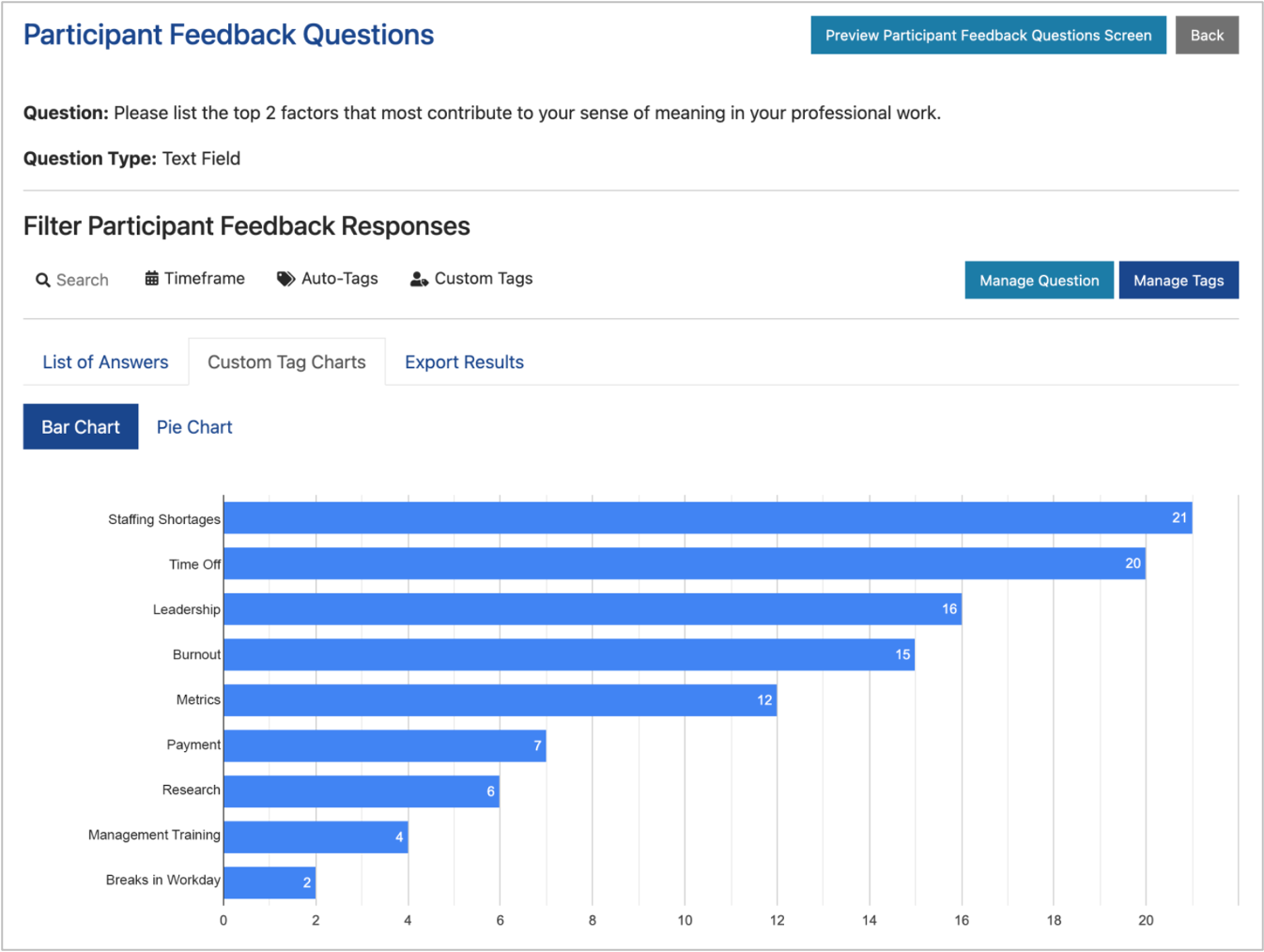
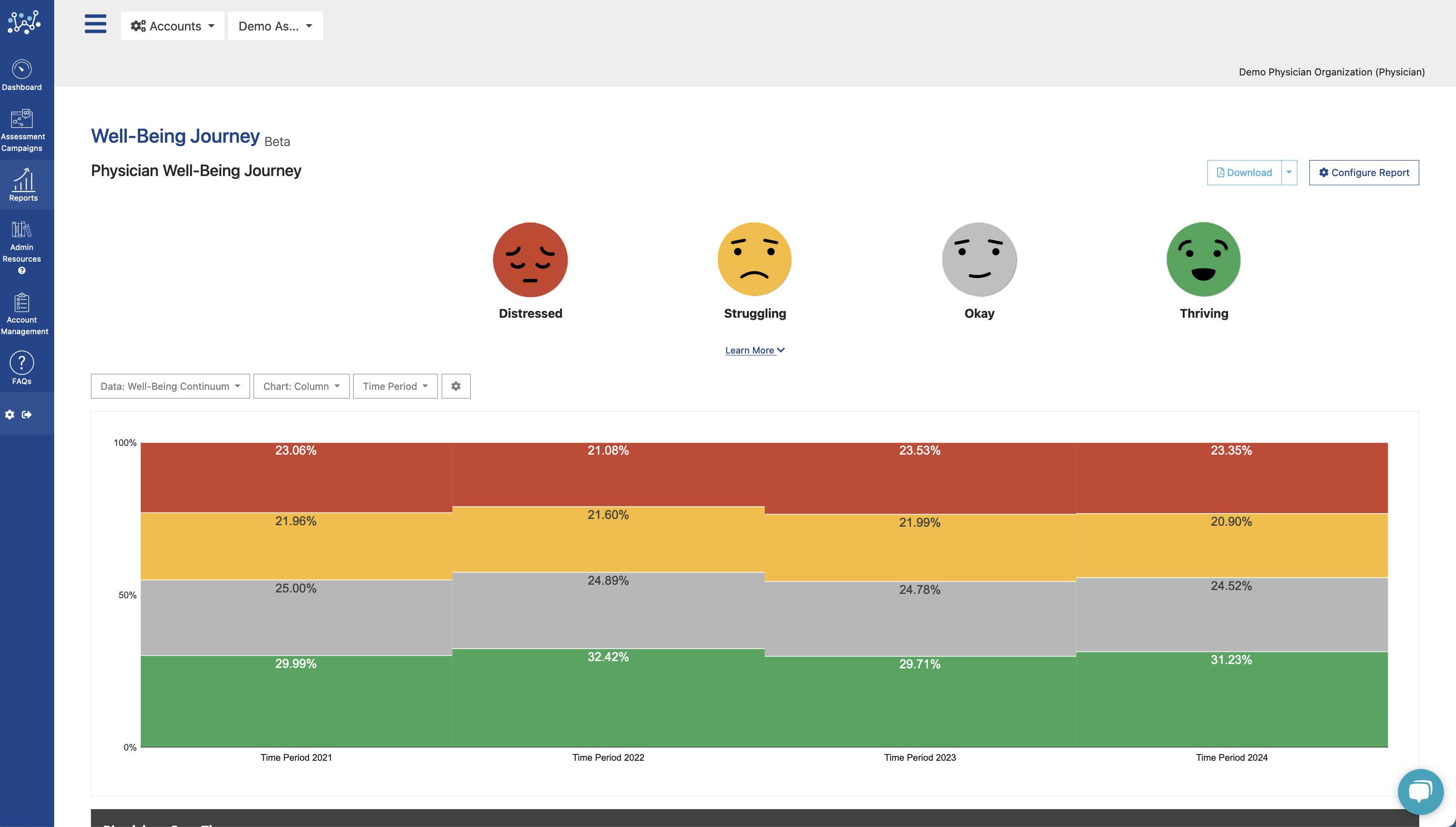
Nurse burnout — frustration and fatigue as a result of stress in the workplace — has a direct impact on patients. Research shows that patients reported lower levels of satisfaction in medical institutions where nurses were unhappy with their work conditions. Now, more institutions are trying to improve well-being among health care staff. Here are seven ways they achieve this.
1. Encourage Your Staff to Exercise Regularly
Countless studies suggest a correlation between exercise and stress, so encouraging your staff to work out more frequently could reduce the effects of burnout. Exercise increases endorphins — the body’s feel-good neurotransmitters — enhances mood and improves sleep quality. One study notes that institutions that provide access to regular exercise programs — at an on-site gym, perhaps — have the potential to prevent nurse burnout.
2. Encourage Your Staff to Eat Healthily
Long shifts often result in poor eating habits. Prevent your staff from consuming sugary snacks at work by introducing healthy food options — something that could increase well-being. The American Nurses Association recommends nurses should limit caffeine intake, restrict vending machine snacks and schedule regular mealtimes.
3. Foster Better Communication
Nurse managers play an important role in burnout prevention, according to Sean M. Herrin from Piedmont College. Therefore, nurses should meet with their managers regularly to discuss the demands of the job and various methods to boost well-being. Other ways to improve communication include regular surveys (either paper or Web-based), group meetings and performance reviews.
RELATED: Everything You’ve Ever Wanted to Know about Nurse Burnout
4. Start Resilience Training
Resilience training — where health care workers learn to adapt to stressors more effectively — has been linked to lower burnout in nurses who work in intensive care units. Programs that incorporate psychological resilience techniques provide nurses with coping tactics that prevent stress, anxiety and depression. This type of training has long been associated with the military but is now frequently used in medical environments.
5. Promote Self-Awareness and Emotional Intelligence
Self-awareness and emotional intelligence are two coping strategies that nurses often use in stressful work situations. Research shows that nurses who have a “positive emotion-focused” strategy — where they reflect on problems and stressors — might deal with burnout better than nurses who don’t. You can encourage better self-awareness and emotional intelligence through a series of training programs.
6. Organize Social Activities at Work
A work-life balance is important in every discipline. Social activities promote better interaction between health care staff and improve well-being. It might be difficult to organize a social event for all your staff, especially when nurses work night shifts, but doing so has multiple benefits. Some group activity ideas include theme days, workplace awards, daily fun routines, weekly competitions and fundraising drives.
7. Practice Meditation
Practicing meditation with your staff lowers stress levels and could result in happier employees. Some of the benefits of meditation for nurses include mindfulness — a reflective, relaxed mental state. In 2015, medical students at Montreal’s McGill University took part in a mandatory mindful medical practice program, which was previously offered only as an elective module
Monitoring nurse well-being enables institutions to detect work dissatisfaction and mental health issues quickly. The Well-Being Index is a simple way to achieve this. The anonymous online self-assessment tool evaluates well-being among health care workers and provides nurses with the resources they need to reduce stress. Try a free demo today.